Assessment of neuroendocrine dysfunction following traumatic brain injury.
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
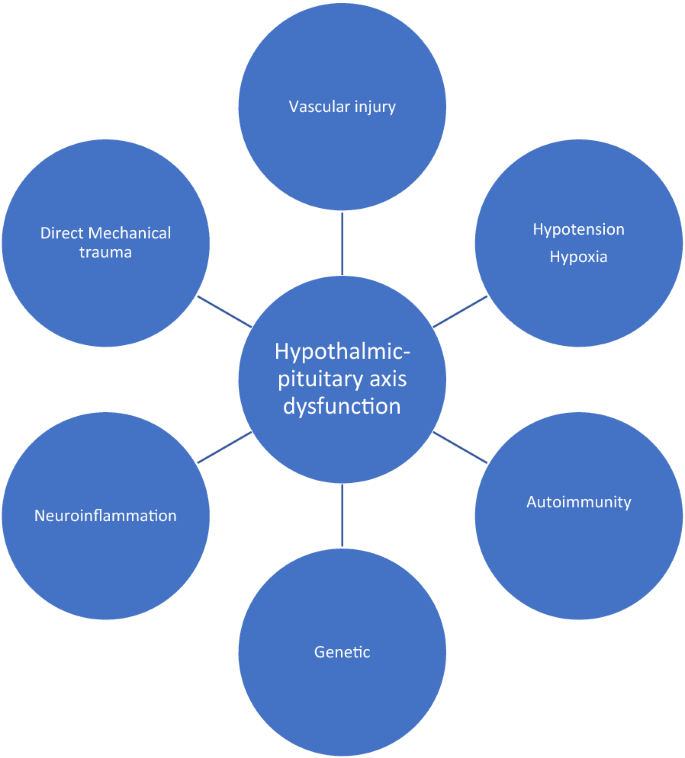
A screening protocol adapted for selected patients at risk for endocrine problems is described, and physicians should be aware of the importance of neuroendocrine dysfunction following TBI. Posttraumatic neuroendocrine pathology may be a clinically significant complication following traumatic brain injury TBI. Metabolic abnormalities are described after TBI in two cases. A 21 year old male injured in a motor vehicle accident admitted in a minimally responsive condition presented with fluctuating high sodium levels, undetectable serum testosterone, and depressed cortisol and thyroid function. Imaging revealed near complete avulsion of the pituitary stalk leading to panhypopituitarism. A 38 year old male admitted for occipital skull fractures and brain contusions presented with hypona tremia and low serum testosterone. Both patients required hormonal replacement and correction of electrolyte abnormalities. A screening protocol adapted for selected patients at risk for endocrine problems is described. While neuroendocrine screening is not advocated in all TBI patients, physicians should be aware of the importance of neuroendocrine dysfunction following TBI.
Endocrine Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury: An Ignored Clinical Syndrome?
Classification and Complications of Traumatic Brain Injury: Practice Essentials, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology
Frontiers The Outcome of Neurorehabilitation Efficacy and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury
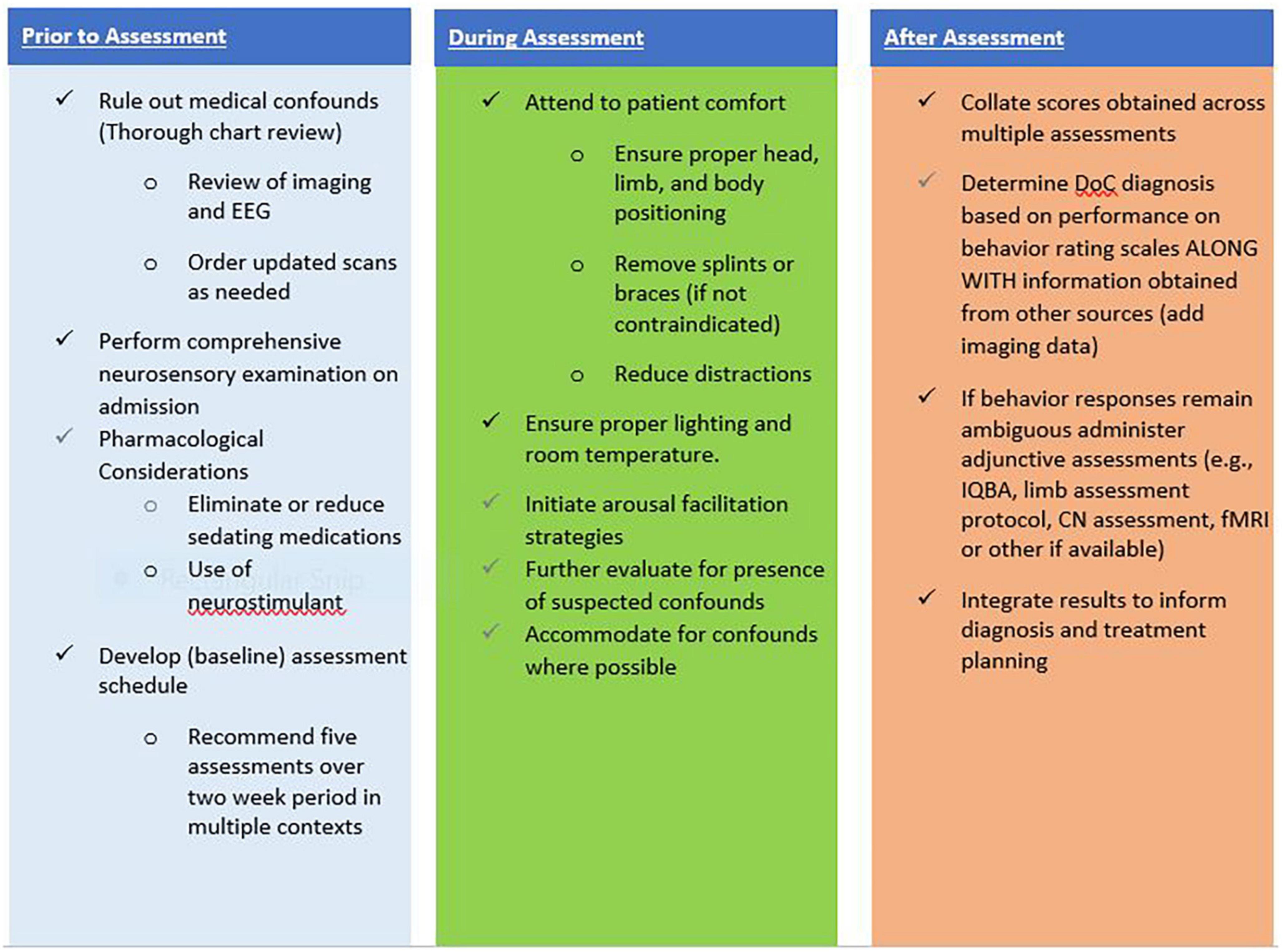
Frontiers Clinical application of recommendations for neurobehavioral assessment in disorders of consciousness: an interdisciplinary approach
PDF) Traumatic Injury to the Brain and Endocrine Evaluation of the Anterior Pituitary a Year After the Event (The TRIBE Study)
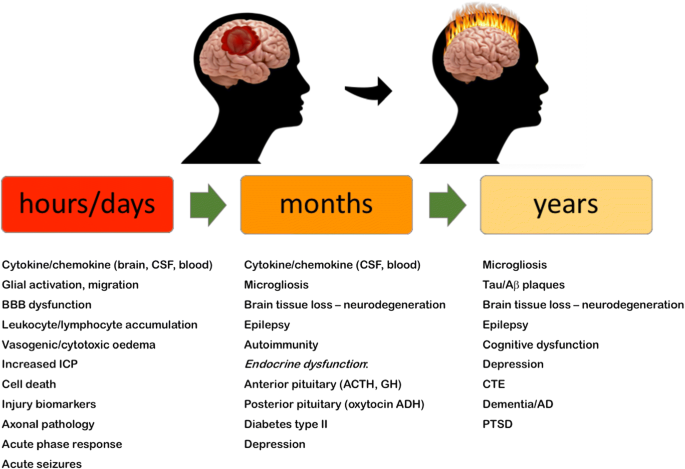
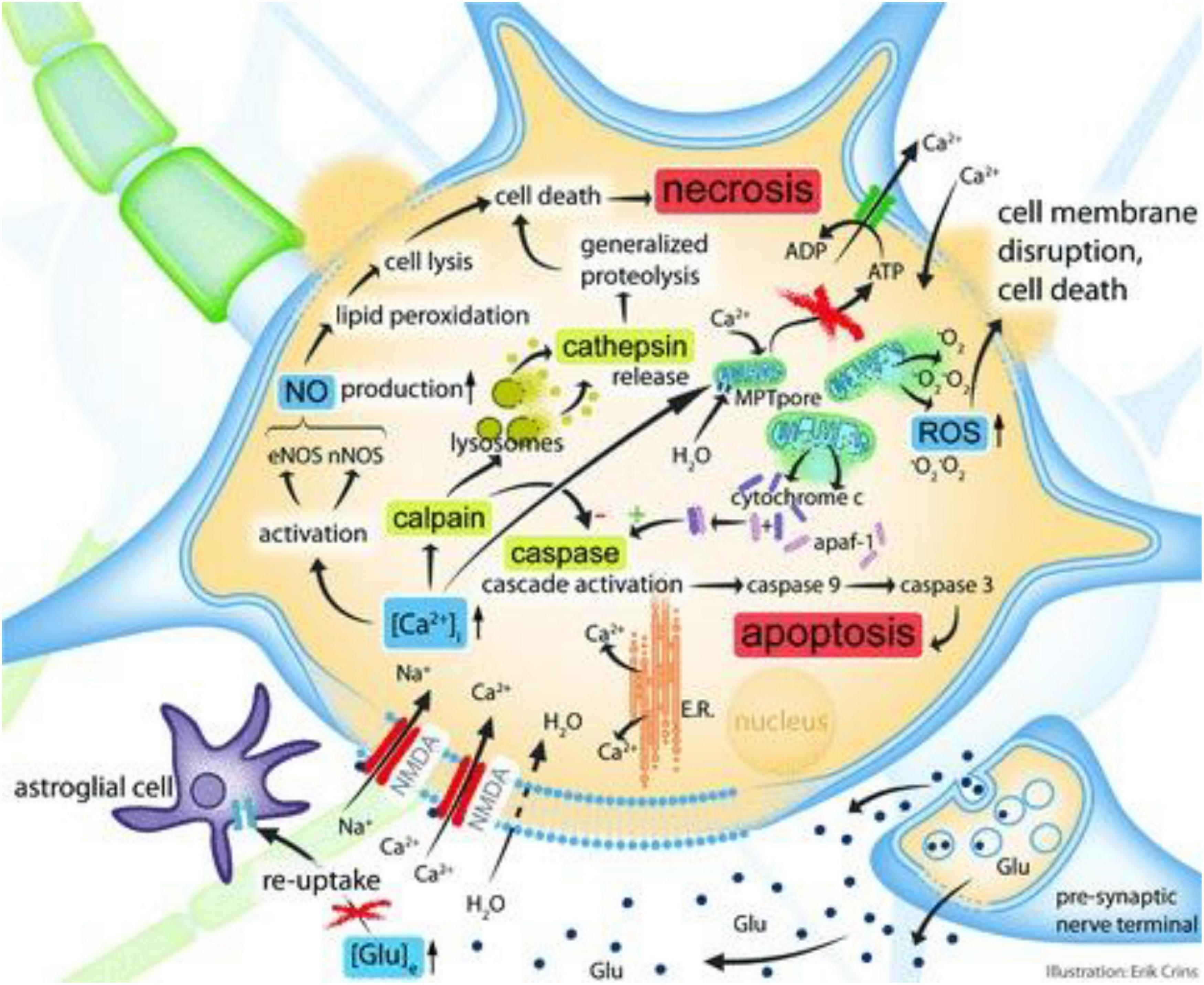
The complexity of neuroinflammation consequent to traumatic brain injury: from research evidence to potential treatments
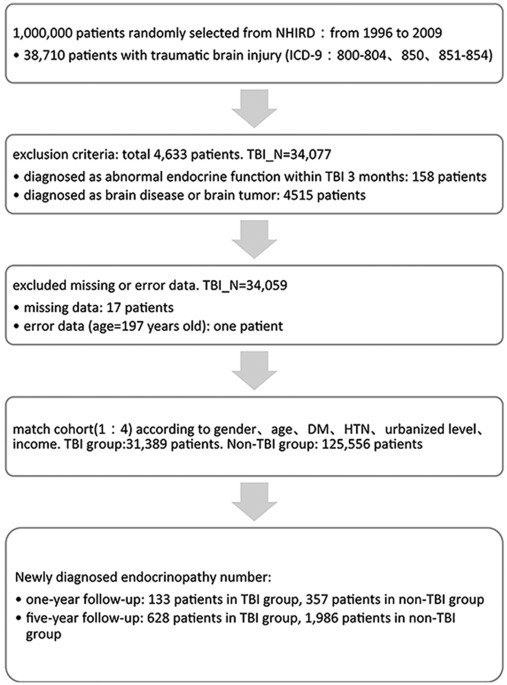
Endocrine dysfunction following traumatic brain injury: a 5-year follow-up nationwide-based study
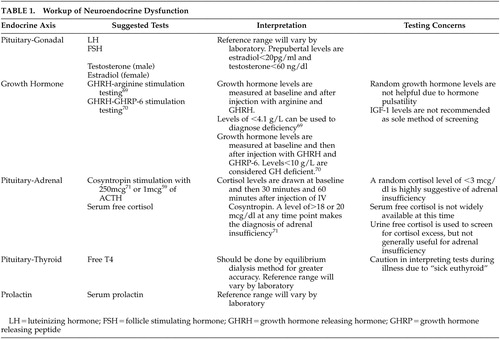
The Neuroendocrine Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences
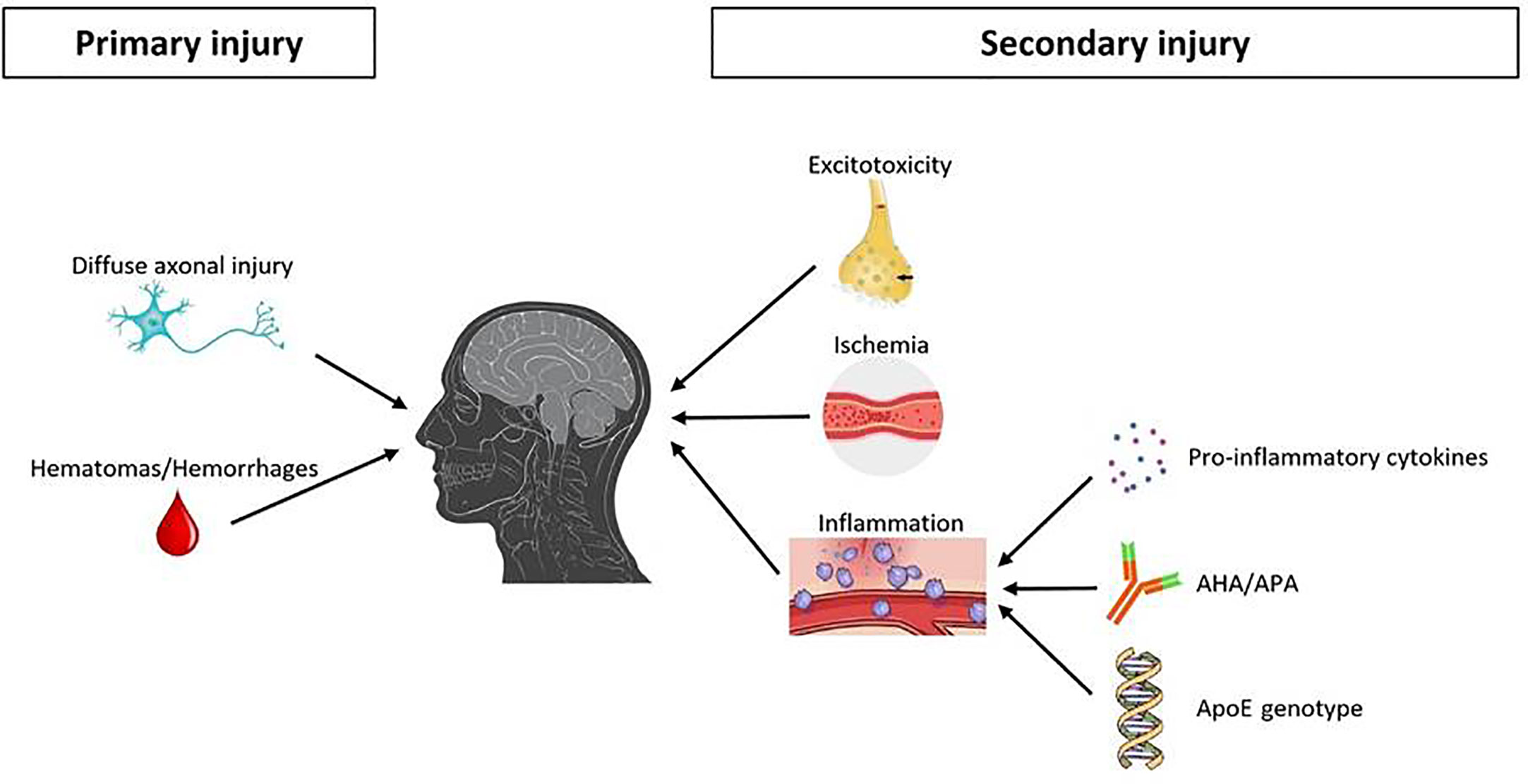
Frontiers Traumatic Brain Injury as Frequent Cause of Hypopituitarism and Growth Hormone Deficiency: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment

Assessment of neuroendocrine dysfunction following traumatic brain injury.
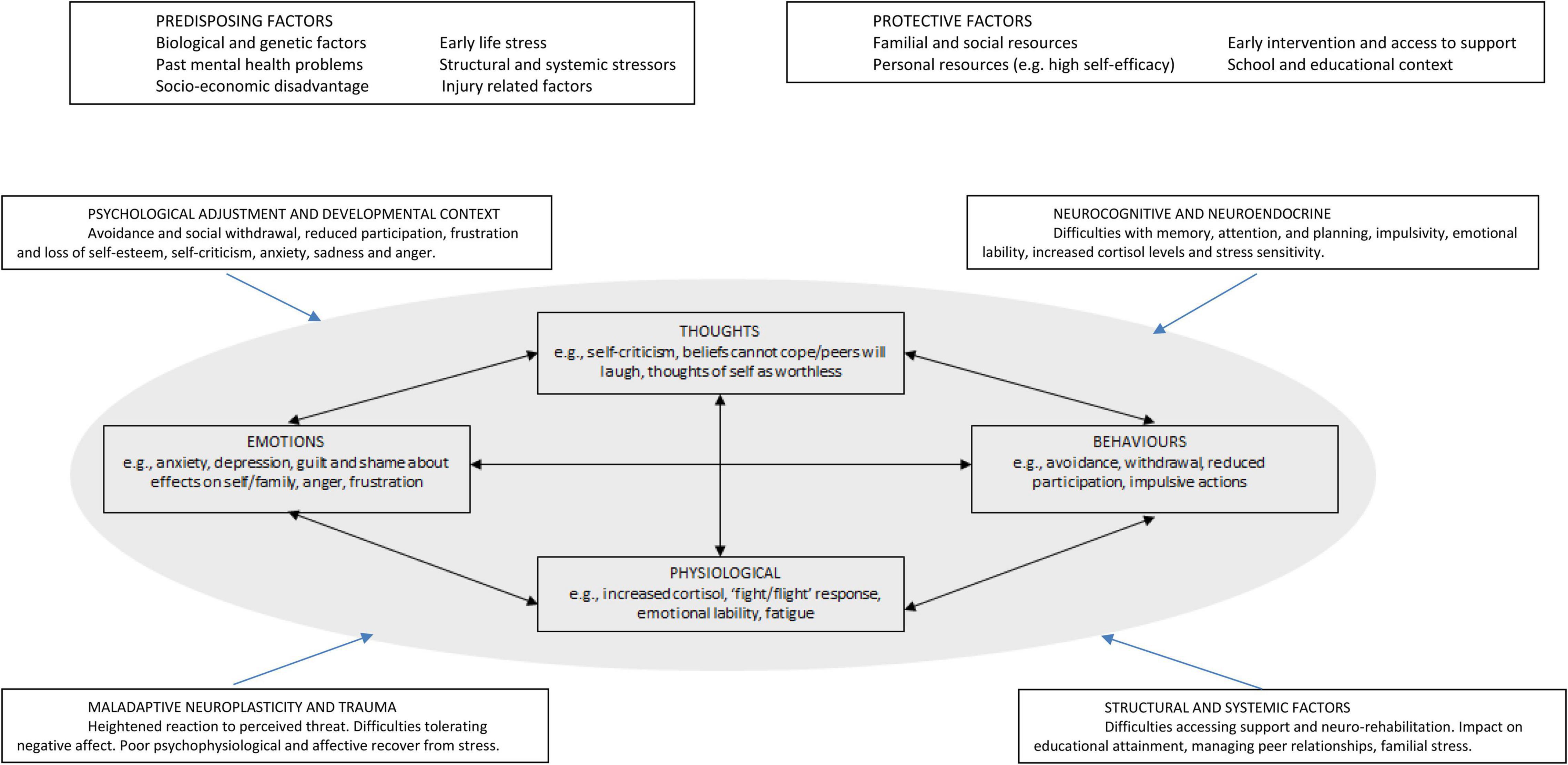
Frontiers Mood Disorders in Young People With Acquired Brain Injury: An Integrated Model
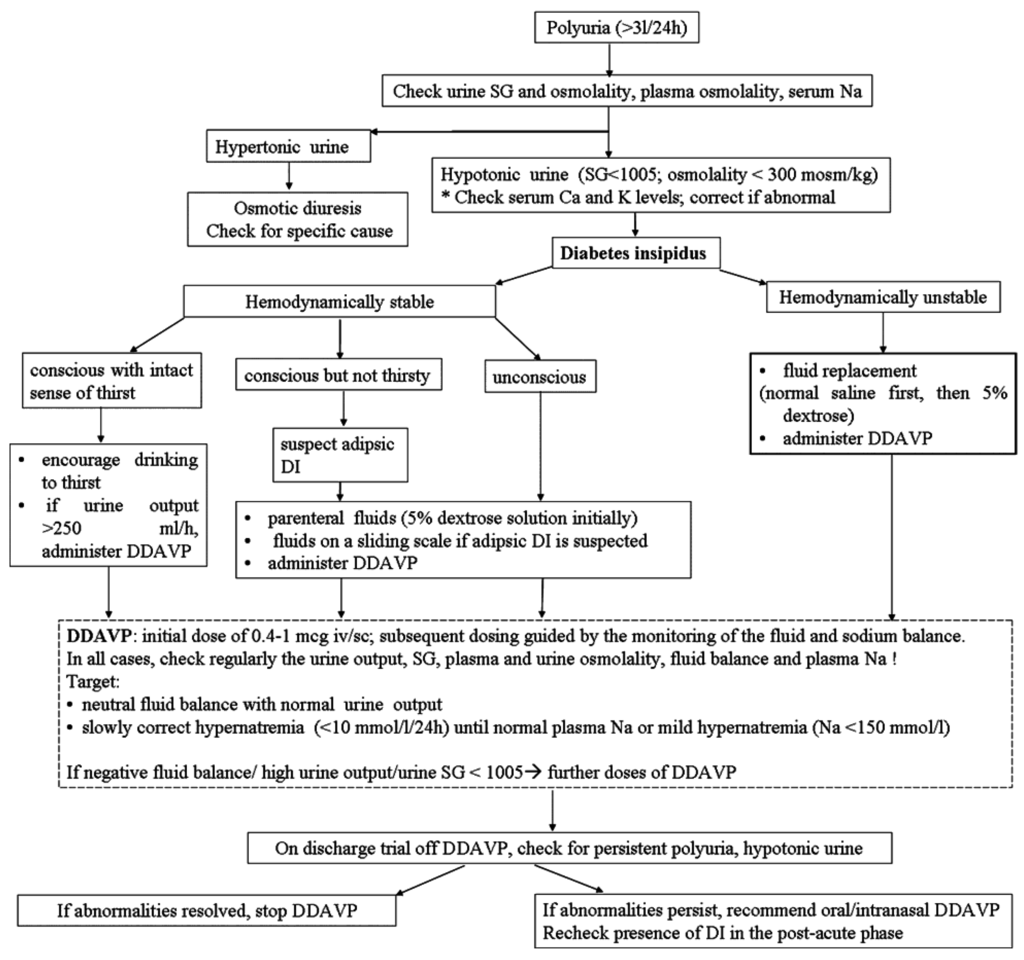
JCM, Free Full-Text
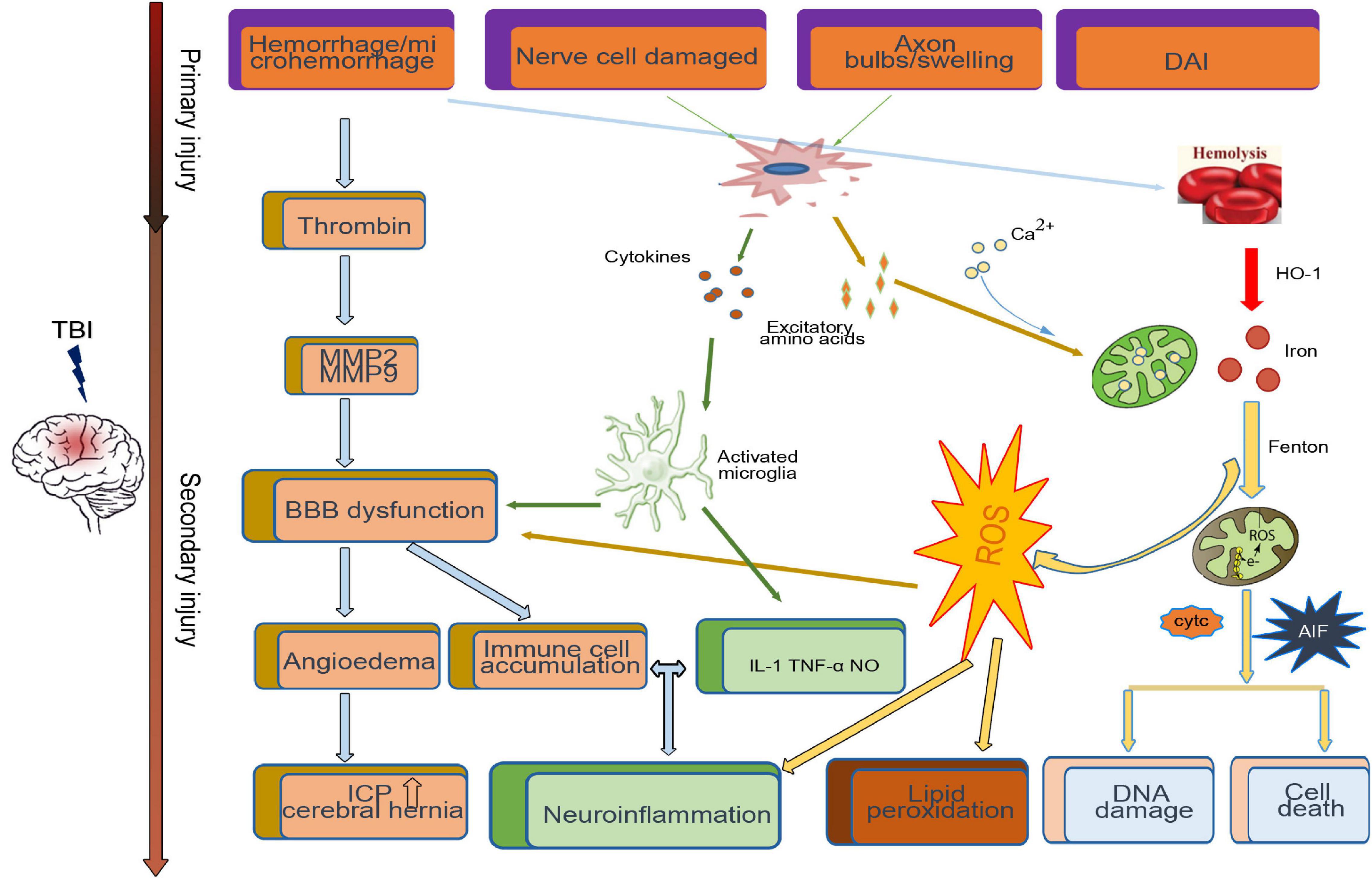
Frontiers Iron Metabolism Disorders for Cognitive Dysfunction After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
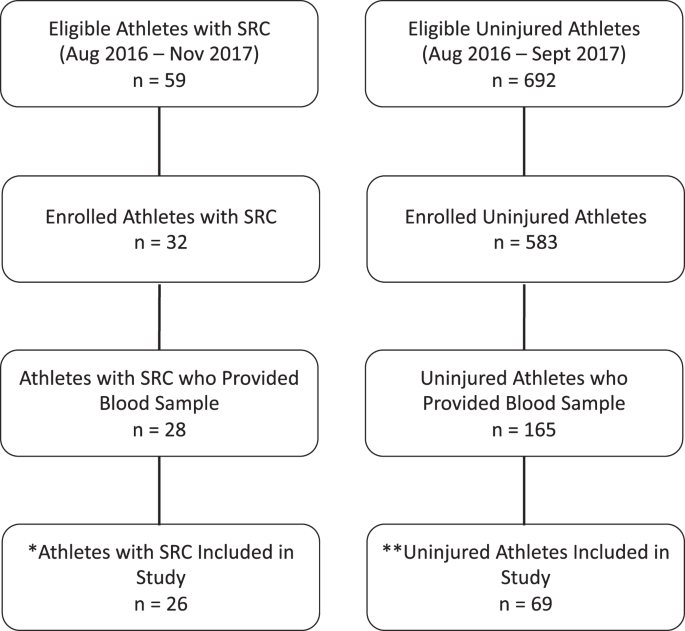
Peripheral blood neuroendocrine hormones are associated with clinical indices of sport-related concussion
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)