Voluntary and forced exposure to ethanol vapor produces similar
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
A major limitation of the most widely used current animal models of alcohol dependence is that they use forced exposure to ethanol including ethanol-c…

Voluntary and forced exposure to ethanol vapor produces similar escalation of alcohol drinking but differential recruitment of brain regions related to stress, habit, and reward in male rats - ScienceDirect

LHb eCB-degrading enzyme inhibition or CB1 receptor activation
Frontiers Adolescent Ethanol Exposure: Anxiety-Like Behavioral Alterations, Ethanol Intake, and Sensitivity
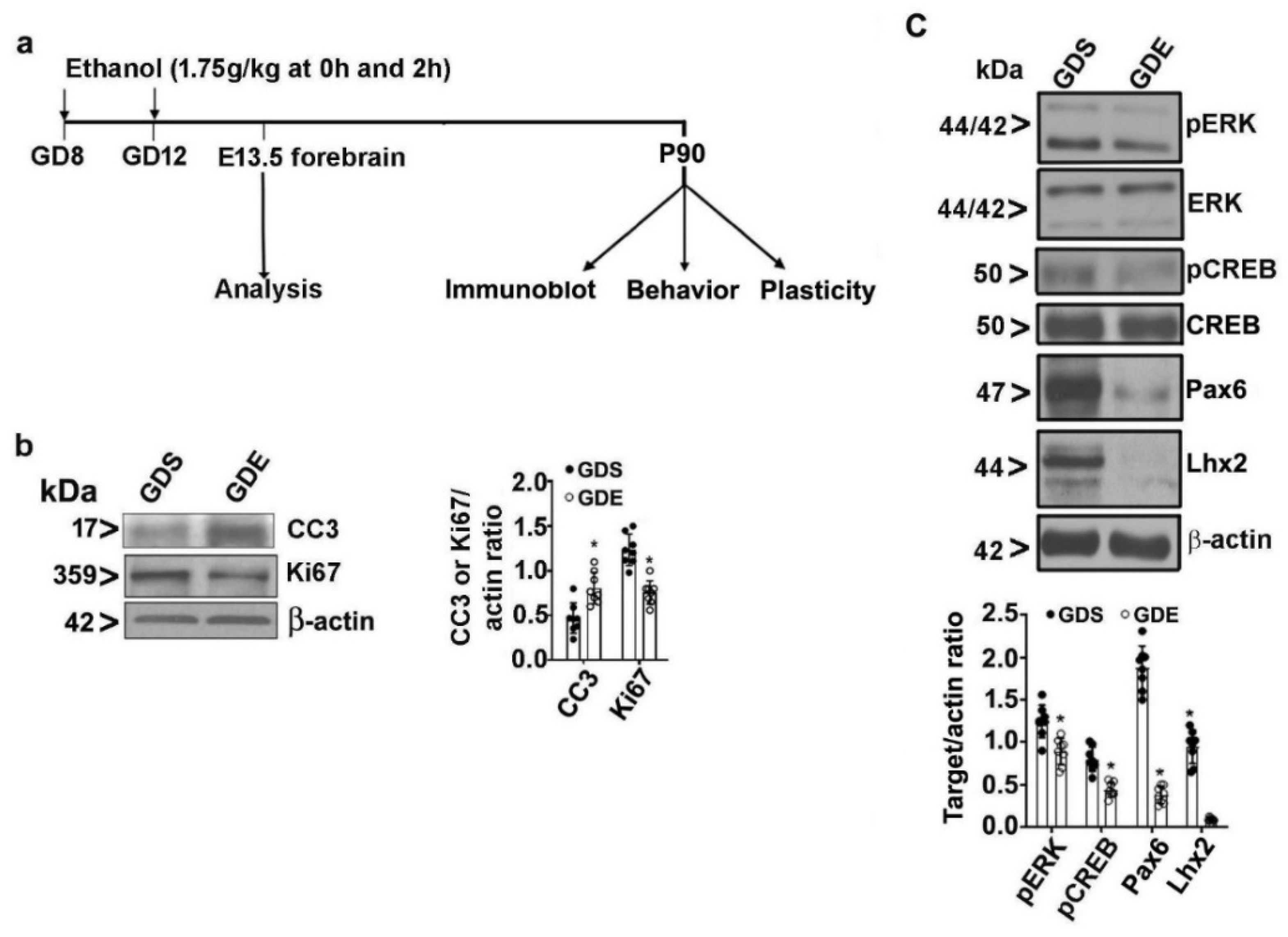
Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text

Cells, Free Full-Text
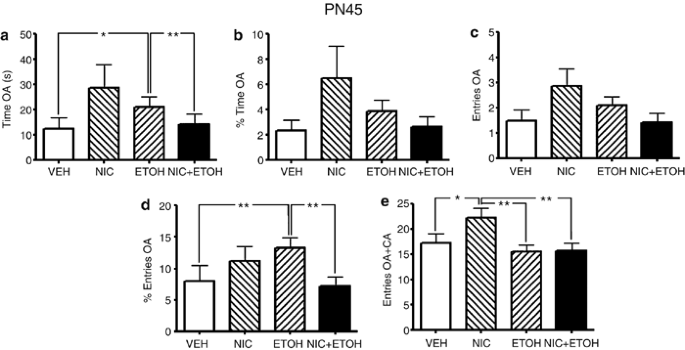
Combined Exposure to Nicotine and Ethanol in Adolescent Mice Differentially Affects Anxiety Levels during Exposure, Short-Term, and Long-Term Withdrawal
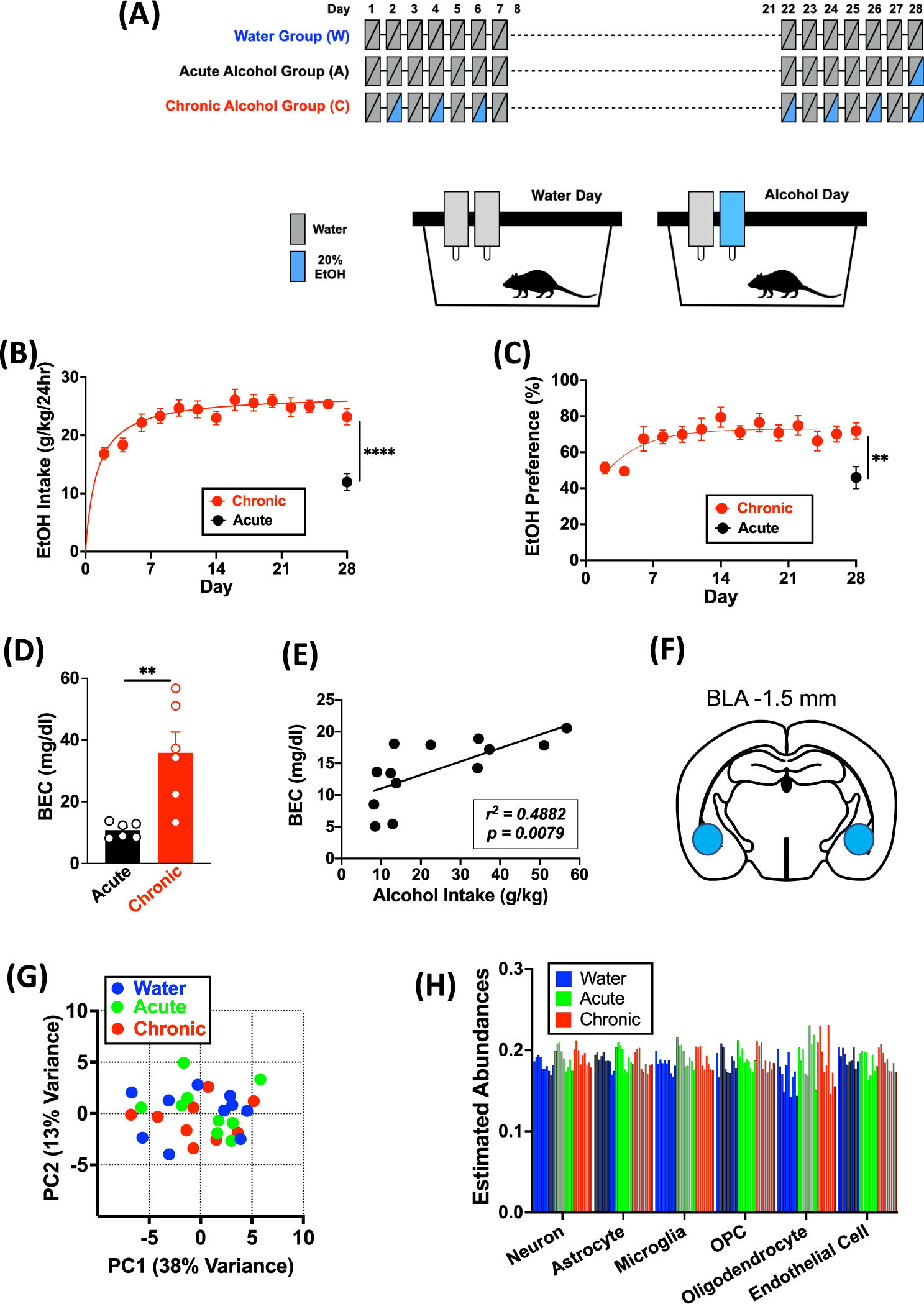
Genome-wide transcriptomics of the amygdala reveals similar oligodendrocyte-related responses to acute and chronic alcohol drinking in female mice
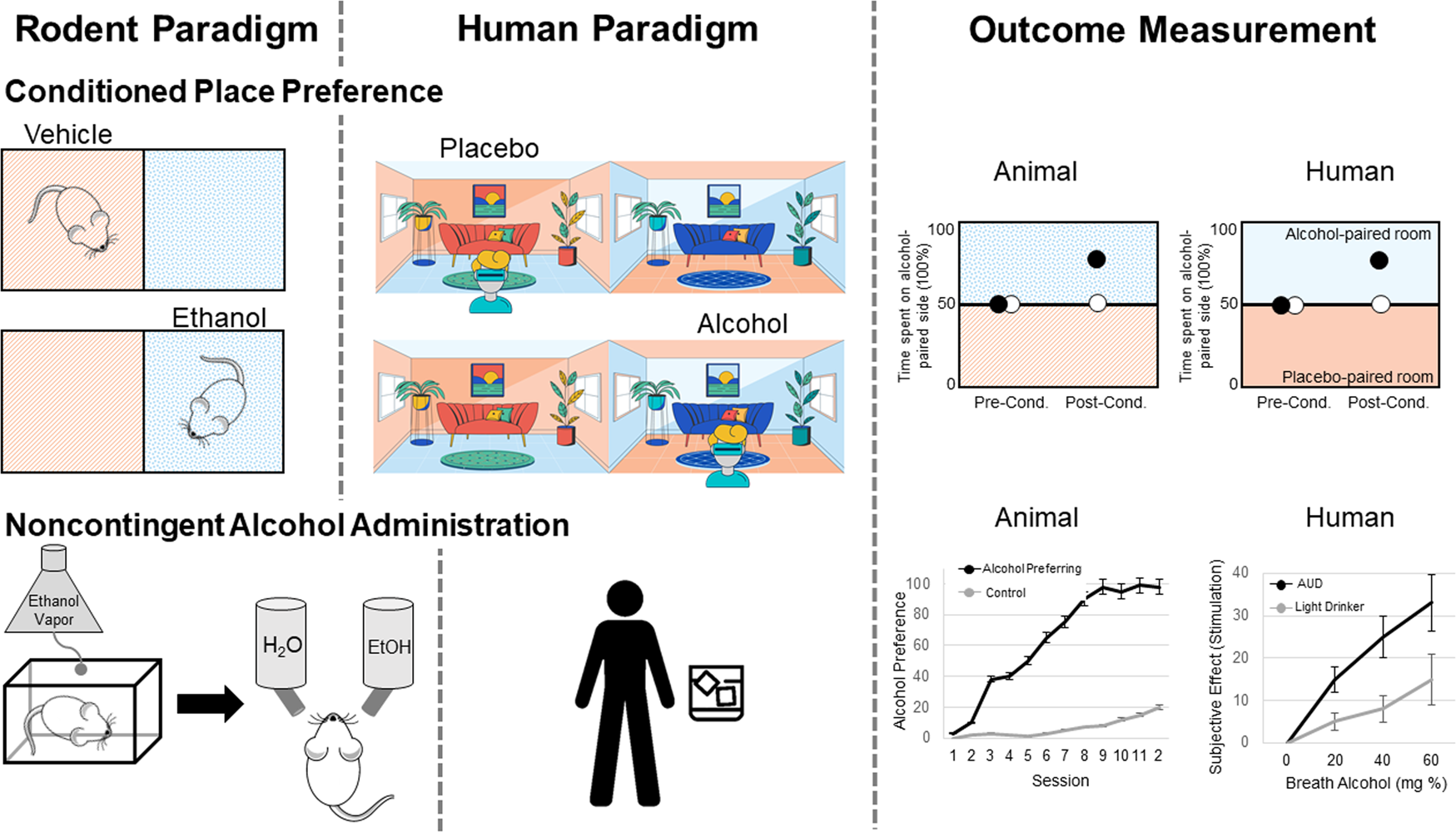
Translational opportunities in animal and human models to study alcohol use disorder

CRF1 receptor-dependent increases in irritability-like behavior during abstinence from chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure

Timing Eclipses Amount: The Critical Importance of Intermittency in Alcohol Exposure Effects - Spear - 2020 - Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research - Wiley Online Library

Neonatal alcohol exposure augments voluntary ethanol intake in the absence of potentiated anxiety-like behavior induced by chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure - ScienceDirect
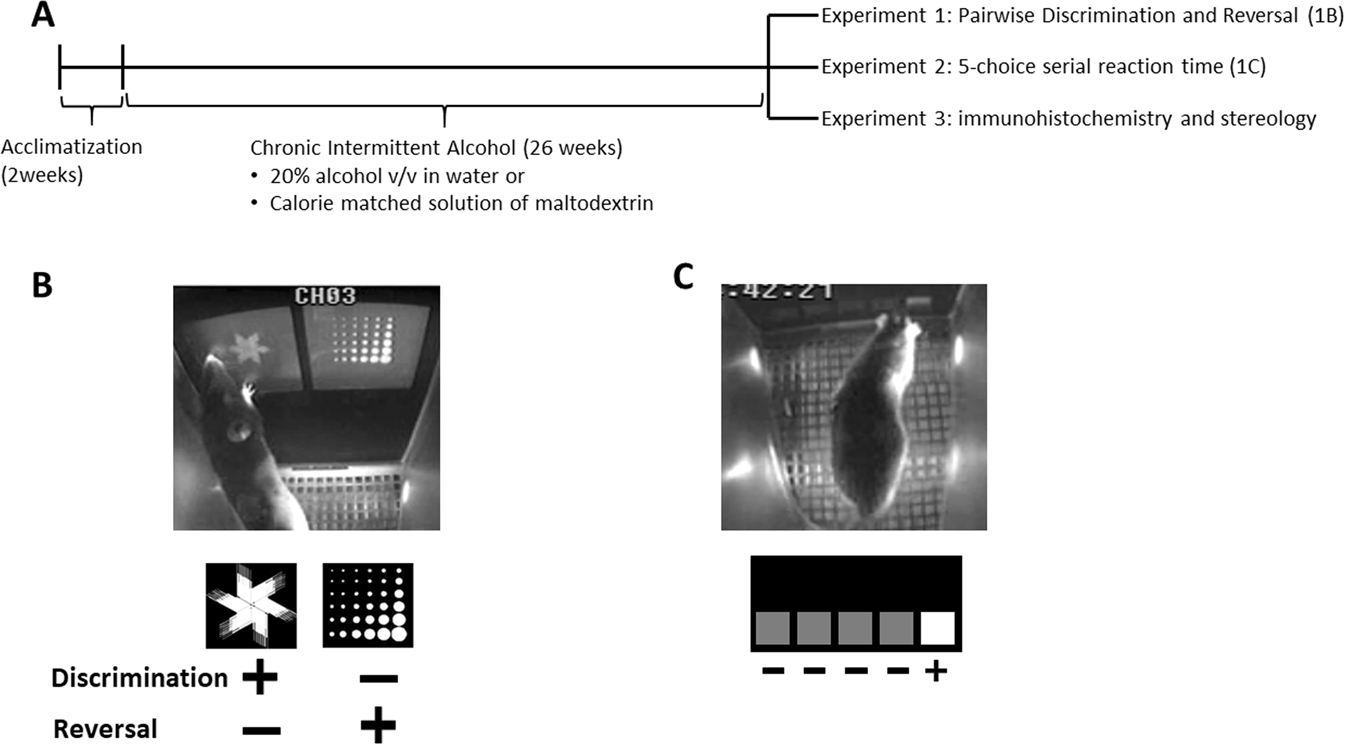
Chronic voluntary alcohol consumption causes persistent cognitive deficits and cortical cell loss in a rodent model
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)