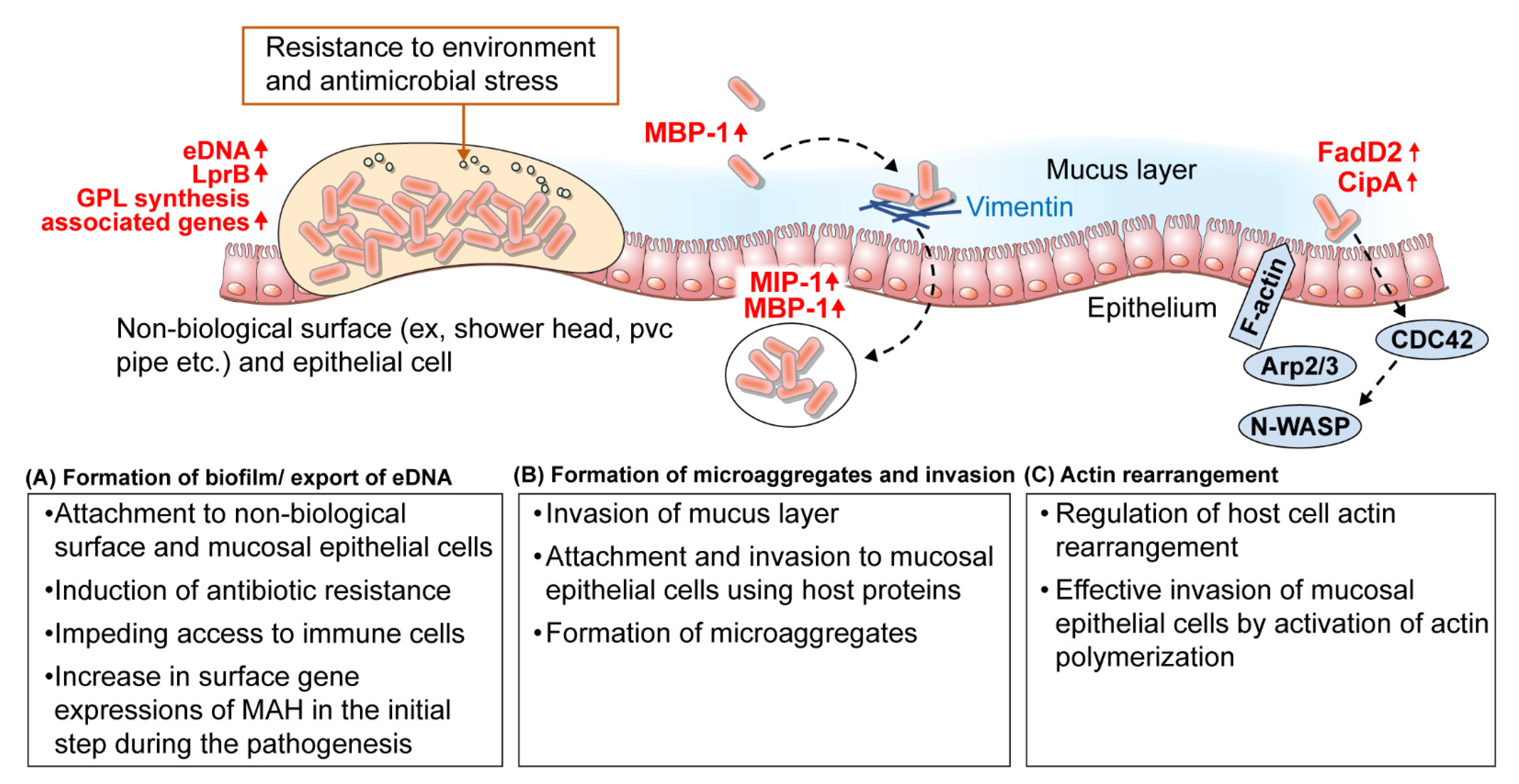
Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Global warming threatens reef-building corals with large-scale bleaching events; therefore, it is important to discover potential adaptive capabilities for increasing their temperature resistance before it is too late. This study presents two coral species (Platygyra verweyi and Isopora palifera) surviving on a reef having regular hot water influxes via a nearby nuclear power plant that exhibited completely different bleaching susceptibilities to thermal stress, even though both species shared several so-called “winner” characteristics (e.g., containing Durusdinium trenchii, thick tissue, etc.). During acute heating treatment, algal density did not decline in P. verweyi corals within three days of being directly transferred from 25 to 31 °C; however, the same treatment caused I. palifera to lose < 70% of its algal symbionts within 24 h. The most distinctive feature between the two coral species was an overwhelmingly higher constitutive superoxide dismutase (ca. 10-fold) and catalase (ca. 3-fold) in P. verweyi over I. palifera. Moreover, P. verweyi also contained significantly higher saturated and lower mono-unsaturated fatty acids, especially a long-chain saturated fatty acid (C22:0), than I. palifera, and was consistently associated with the symbiotic bacteria Endozoicomonas, which was not found in I. palifera. However, antibiotic treatment and inoculation tests did not support Endozoicomonas having a direct contribution to thermal resistance. This study highlights that, besides its association with a thermally tolerable algal symbiont, a high level of constitutive antioxidant enzymes in the coral host is crucial for coral survivorship in the more fluctuating and higher temperature environments.

Activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) of non-inoculated (control) and
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase - an overview

Scavenging ROS: Superoxide Dismutase/Catalase Mimetics by the Use of an Oxidation-Sensitive Nanocarrier/Enzyme Conjugate
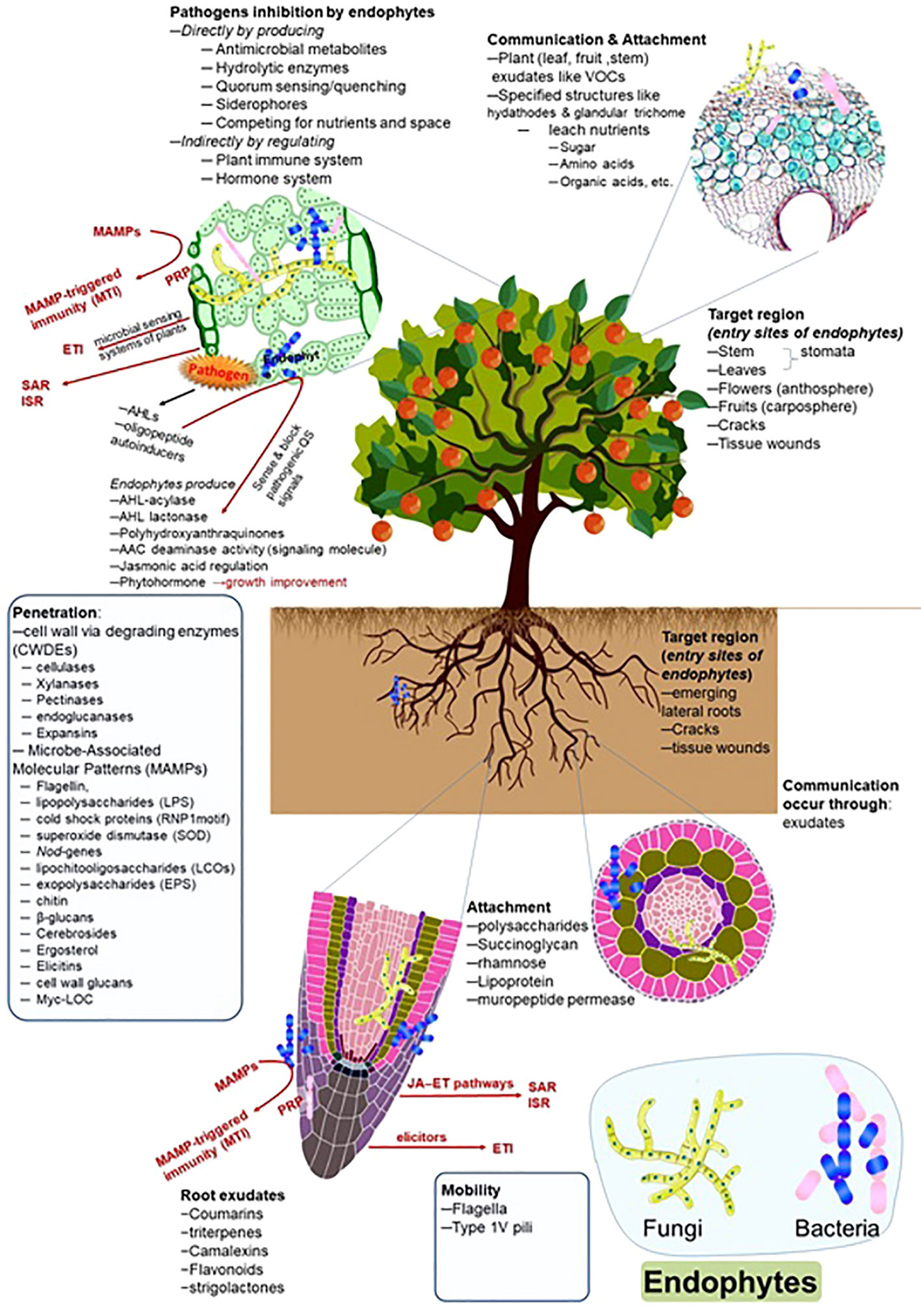
Frontiers Deciphering the role of endophytic microbiome in postharvest diseases management of fruits: Opportunity areas in commercial up-scale production

Superoxide Dismutase - an overview

MDA, GSH, NO levels and SOD, CAT, and TF activities of lung tissue.

The family of SOD enzymes in microbial pathogens. In a gram-negative

Insights into host–pathogen interactions from state‐of‐the‐art animal models of respiratory Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections - Lorenz - 2016 - FEBS Letters - Wiley Online Library

Small-molecule superoxide dismutase (SOD)1 inhibitors. Shown are three

Human CD4+CD25+ T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor against aberrant superoxide dismutase 1 trigger antigen-specific immunomodulation - Cytotherapy

An insight on superoxide dismutase (SOD) from plants for mammalian health enhancement - ScienceDirect

Hint from an Enzymatic Reaction: Superoxide Dismutase Models Efficiently Suppress Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






